MAC Address Complete Guide

Ethernet 2
Mac address is the most important part of Ethernet 2 protocol. MAC addresses are used to send Ethernet frames between two stations in the same local area network. Each station has a unique MAC address that is used to identify who is the sender (source mac address) and who the receiver (destination mac address) is.
What is mac address
Every NIC (also called LAN card or network card) has a hardware address that's known as a MAC address. The MAC address is sometimes referred to as a networking hardware address. A MAC address is given to a network adapter when it is manufactured. It is hardwired or hard-coded onto your computer's network interface card - NIC and is unique to it. These addresses are used in most network technologies, including Ethernet , Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
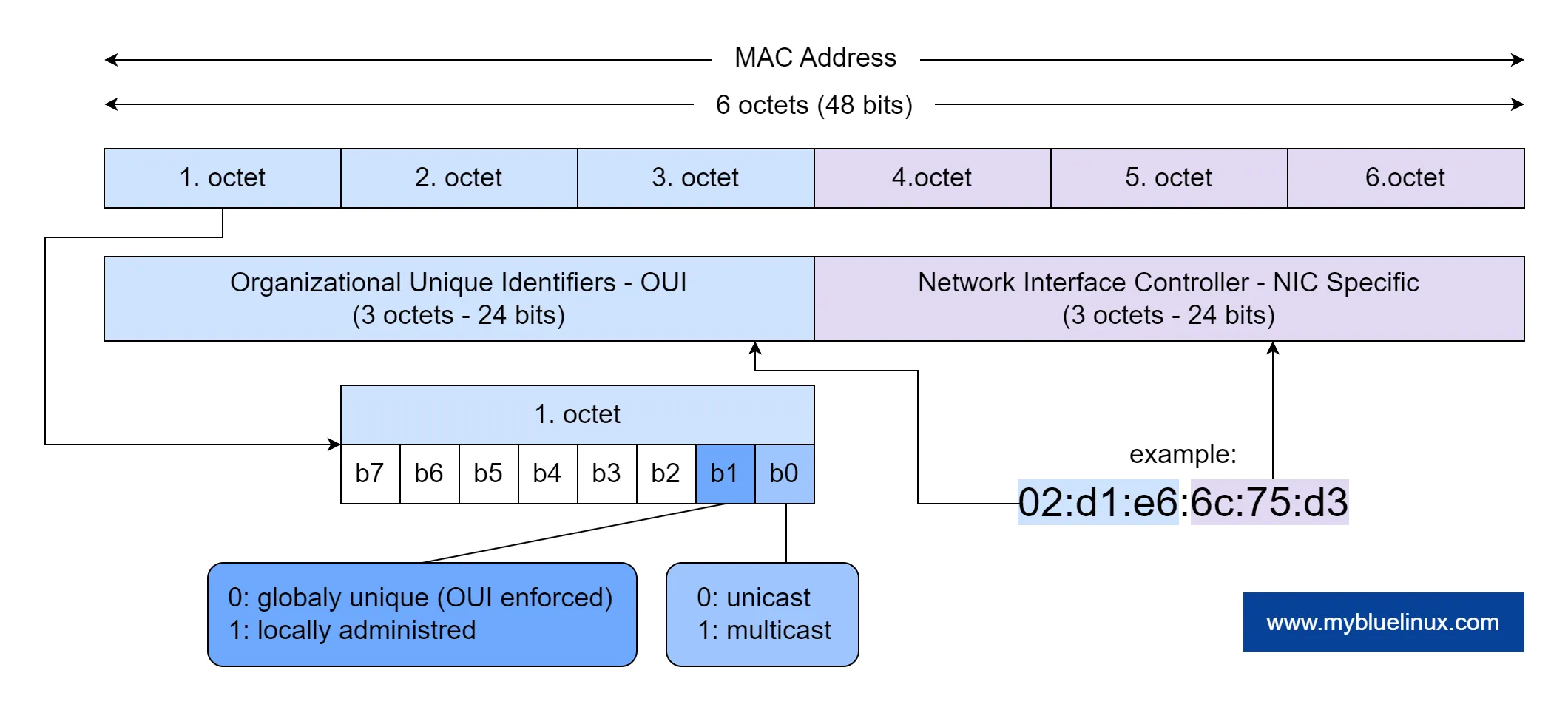
MAC Addresses are 6 bytes (or 48 bits long), providing 248 = 281,474,976,710,656 (over 281 trillion) addresses in theory. In order to make these addresses easier for humans to remember, these addresses are usually written as six two-digit hexadecimal numbers, such as 01:23:45:67:89:AB. Some other, less common notations may write the same MAC address as: 01:23:45:67:89:ab, 01-23-45-67-89-AB, or 0123.4567.89ab.
MAC Address Format
For example, consider a network adapter with the MAC address "02:d1:e6:6c:75:d3". The OUI for the manufacture of this NIC adapter is the first three octets: "02:d1:e6". The remaining three octets (24 bits): "6c:75:d3" represent the device’s unique identifier assigned by the manufacturer.
Unicast vs. multicast (I/G bit)
The least significant bit of an address's first octet is referred to as the I/G, or Individual/Group, bit.
| binary | HEX | DECIMAL |
|---|---|---|
| 00000000 | 00 | 0 |
| 00000001 | 01 | 1 |
| 11111111 | FF | 255 |
| 00000010 | 02 | 2 |
| 00000011 | 03 | 3 |
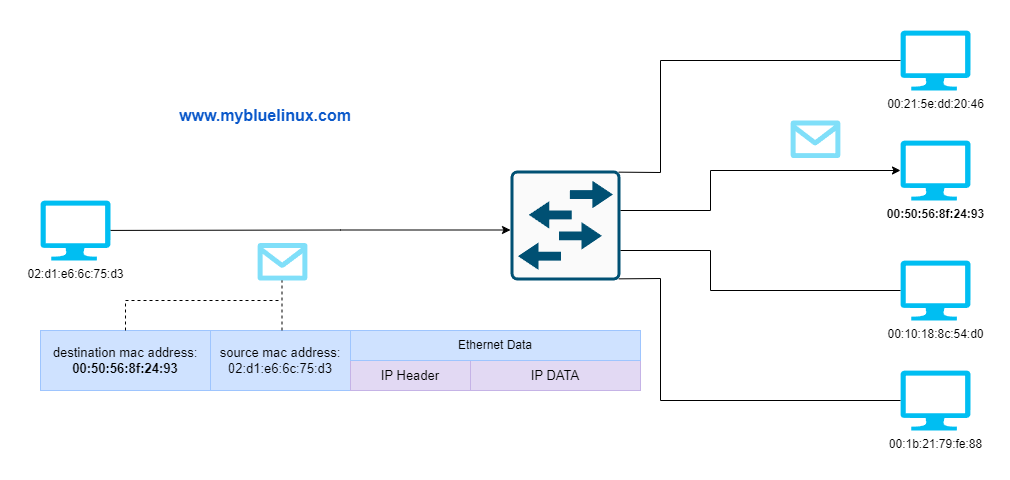
Unicast Frame
When least significant bit is 0 (zero), the frame is meant to reach only one receiving network interface. This type of transmission is called unicast
.
The Unicast MAC address represents the specific NIC on the network. A Unicast MAC address frame is only sent out to the interface which is assigned to a specific NIC and hence transmitted to the single destination device.
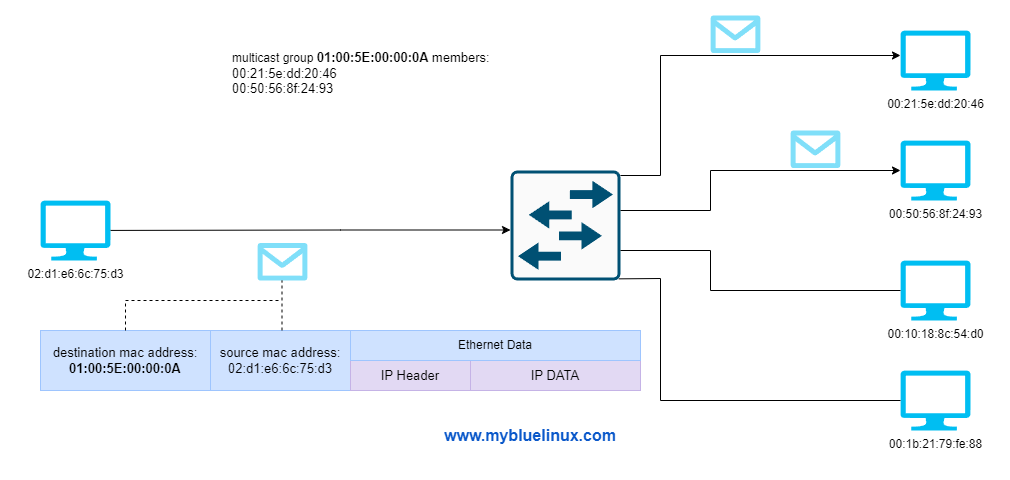
Multicast Frame
If the least significant bit of the first octet is set to 1, the frame is considered as multicast
.
The IEEE has built in several special address types to allow more than one network interface card to be addressed at one time:
- Packets sent to a multicast address are received by all stations on a LAN that have been configured to receive packets sent to that address.
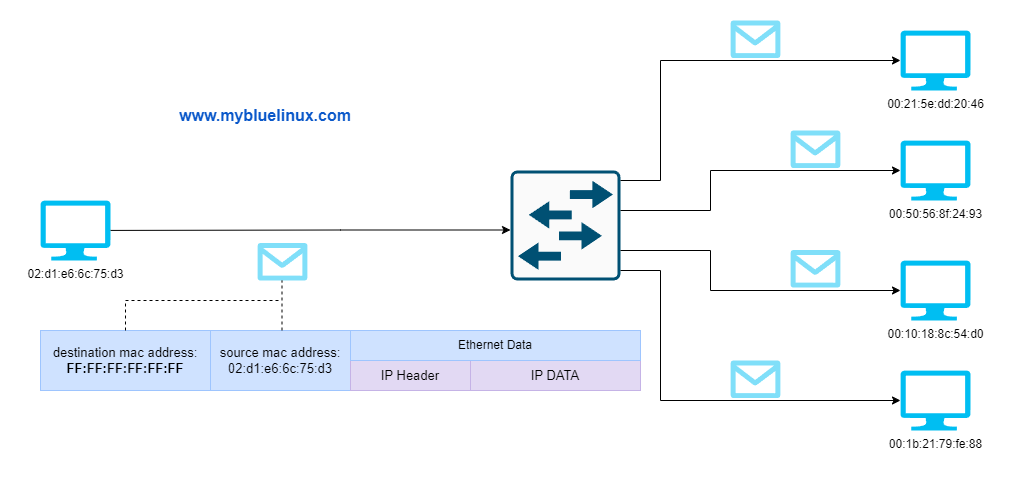
- Packets sent to the broadcast address, all one bits, are received by all stations on a local area network. In hexadecimal the broadcast address would be
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. A broadcast frame is flooded and is forwarded to and accepted by all other nodes.
Broadcast Frame
unicast vs brodcast vs multicast
In contrast, a multicast address is used to address a specific group of devices, and a unicast address is used to address a single device.
Universally Administered MAC Address
UAA is the most used type of MAC address. It is given to the network adapter at the time of manufacturing. The first three octets of Universally Administered Address find the organization / manufacturer that issued the identifier. The remaining octets of the MAC address is assigned by manufacturer.
Locally Administered MAC Address
LAA is an address that changes the MAC address of the adapter. You may assign this address to a device used by network administrator. It overrides the address assigned by device manufacturers. Locally Administered Address does not contain OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier). The full form of LAA is Locally Administered Address. (very rarely used)
Universal addresses that are administered locally
In virtualisation, hypervisors such as QEMU and Xen have their own OUIs. Each new virtual machine is started with a MAC address set by assigning the last three bytes to be unique on the local network. While this is local administration of MAC addresses, it is not an LAA in the IEEE sense.
Changing and Spoofing MAC Addresses
Despite being hard-coded into a device, MAC addresses can be changed or "spoofed" using software. This practice can be useful for protecting privacy, testing networks, or circumventing network restrictions. However, it can also be misused for malicious activities, such as evading tracking or infiltrating protected networks.
How does MAC Addresses Work
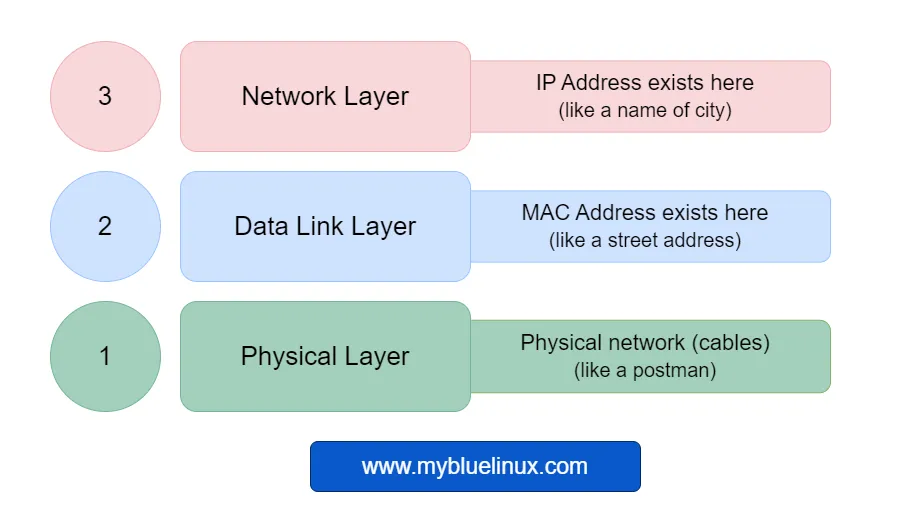
MAC addresses play a crucial role in the data link layer (Layer 2) of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. This model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a communication system into seven distinct categories or "layers."
MAC addresses are used to send Ethernet frames between two stations in the same local area network. Each station has a unique MAC address that is used to identify who is the sender (source mac address) and who the receiver (destination mac address) is. But Ethernet frames can’t travel between networks behind routers. In this way, MAC addresses function like a house’s street address (layer 2) in the city (cities are layer 3): they tell devices where to find and send the information. But letter whithout the name of City (layer 3 - ip address) can’t travel behind city.
mac address summary
- MAC address is the physical address, which uniquely identifies each device on a given network. To make communication between two networked devices, we need two addresses: IP address and MAC address. It is assigned to the NIC (Network Interface card) of each device that can be connected to the internet.
- It stands for Media Access Control, and also known as Physical address, hardware address, or BIA (Burned In Address).
- It is globally unique; it means two devices cannot have the same MAC address (at least cannot have the same MAC address on the same LAN network). It is represented in a hexadecimal format on each device, such as 00:0a:95:9d:67:16.
- It is 12-digit, and 48 bits long (6 bytes), out of which the first 24 bits are used for OUI (Organization Unique Identifier), and 24 bits are for NIC/vendor-specific.
- It works on the data link layer of the OSI model.
- It is provided by the device's vendor at the time of manufacturing and embedded in its NIC.
- The ARP protocol is used to associate a logical address with a physical or MAC address.
- MAC Address can be changed by a software
Why are MAC Addresses Important:
- Device Identification: Each device on a network must have a unique identifier. For most hardware, this unique identifier is the MAC address. It helps to accurately route packets of data from their source to their destination.
- Security: Network administrators can use MAC addresses for security purposes. For instance, they can restrict network access to specific MAC addresses (a technique known as MAC filtering) or track a device’s network activities.
- Troubleshooting: MAC addresses are invaluable in network diagnostics. They can help identify problematic devices, understand network traffic patterns, and resolve connectivity issues.